Maximize clinical utility and sensitivity for your patients
Conventional liquid biopsy technologies only allow you to monitor specific genomic variations. NGS promises to expand your view to panels of genes while maintaining high sensitivity and precision. The process, however, is complex and requires software tailored to your needs.
Achieve
maximum performance
with your assays
Extensive
onboarding and validation included
Comprehensive
quality metrics
and control
Achieving the best analytical performance
When designing an assay several factors must be considered in order to achieve the optimum performance with a specific budget.
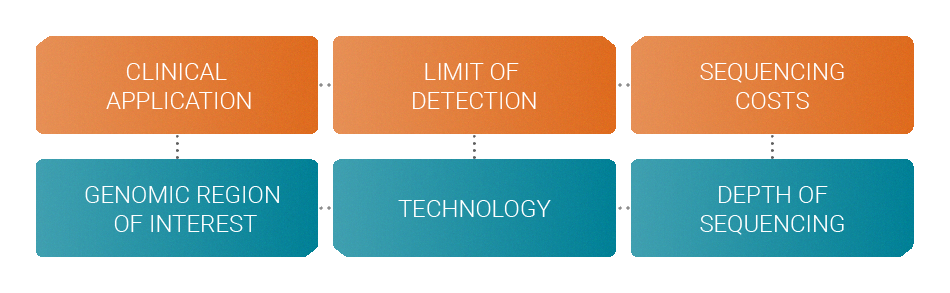
Your clinical application determines the genomic region of interest that should be monitored. The desired limit of detection determines the choice of technology like molecular barcodes. Your budget allows you to sequence at a certain depth. All these factors are interdependent.
Sequencing strategies for different applications
NGS assays are tailored to meet specific requirements. The numbers shown in the table on the right may serve as a guideline. Whichever configuration you choose, the varvis® software allows you to accurately validate your assay and enables you to achieve maximum performance.
The varvis® software supports you in every stage of assay development
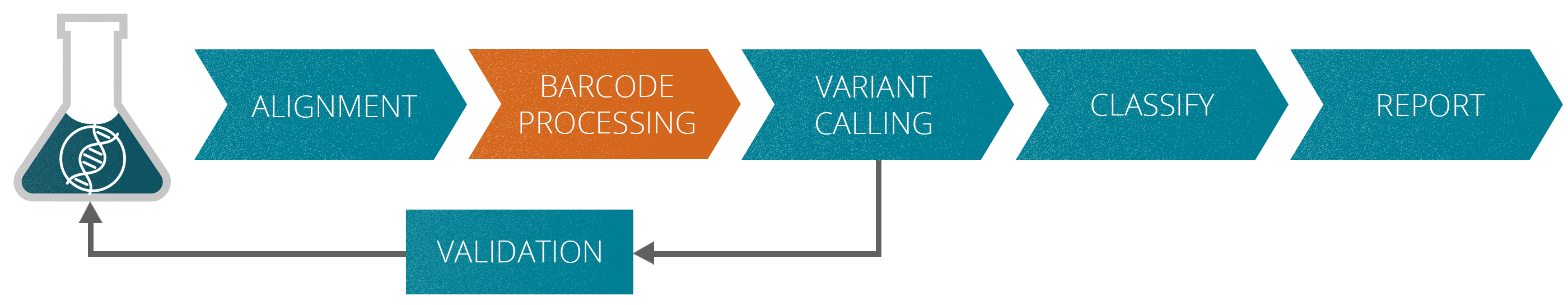
The validation of NGS assays for liquid biopsy applications may be very complex since they are tailored for the specific task. At the beginning of the onboarding process with the varvis® software, your assays are validated according to standardized protocols.
Our on-boarding process includes:
Support in technology selection
Training
Validation of assays
Achieve the highest performance with barcoding
Molecular barcoding allows for improved sensitivity and precision in NGS assays by many orders of magnitude. While the regular error rate in NGS is of the order of 1/100, barcoding technologies enable us to reduce the error rate to 1/10,000 or even 1/10,000,000. The varvis® software is capable of processing different kinds of molecular barcodes and call variants accurately.

Simple monitoring of laboratory processes
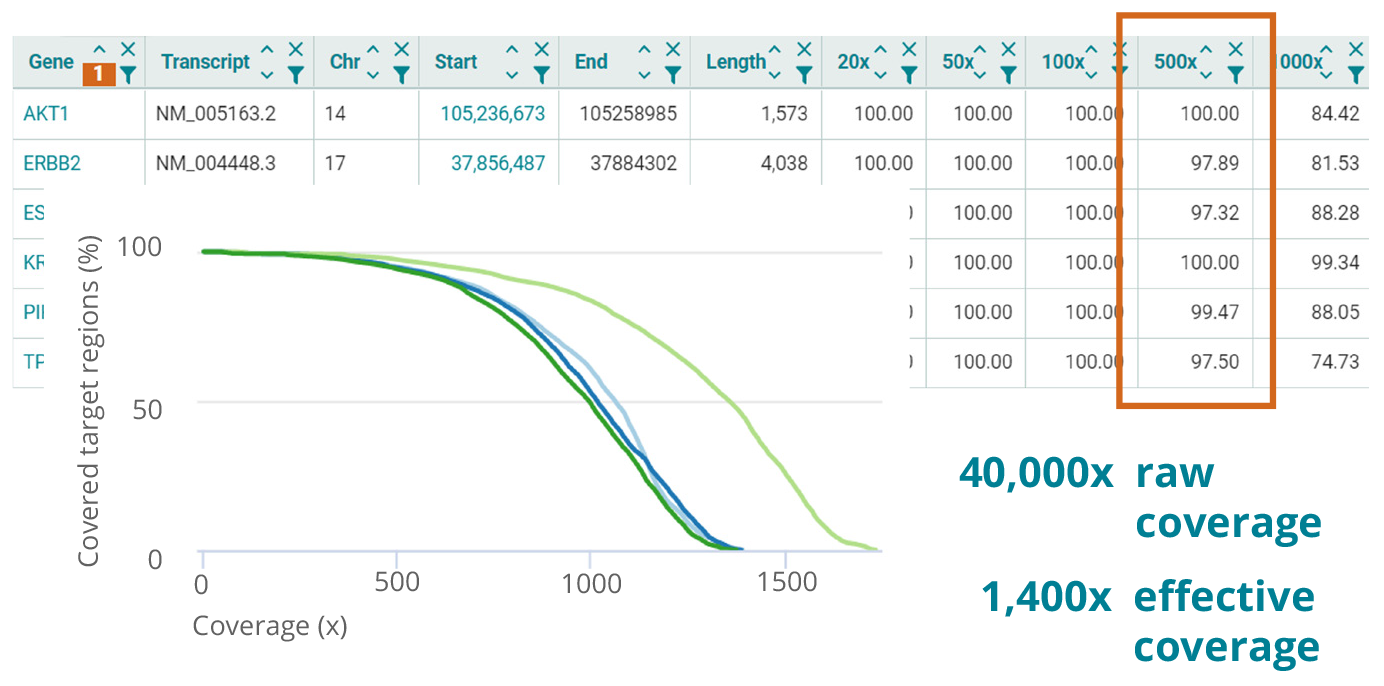
In liquid biopsy applications, you are pushing NGS performance to the limit. It is absolutely crucial that you are able to accurately assess and monitor the performance of your laboratory process. The varvis® QC Service provides a wealth of detailed metrics that allow you to determine any deviations from your target performance so that you can react accordingly early on.
See for yourself how the varvis® software can accelerate your laboratory workflows
and increase your diagnostic yield.
Read more

Watch now: Sharpening our tools for the diagnosis of mosaic disorders
by Nadine Näser, September 9, 2021
In this session, our speakers highlight the specific challenges that physicians encounter while handling mosaic diseases and explain in detail how a suitable assay was established and validated.
Webinar on-demand: Pushing the boundaries The limit of detection in NGS liquid biopsy
NGS laboratories must comply with numerous regulations and guidelines, and strive, at the same time, to deliver the best possible analytical procedures. In this webinar our three speakers will showcase the latest advancements in NGS liquid biopsy technologies and demonstrate how these novel assays can be properly validated and tailored to the specific use case.
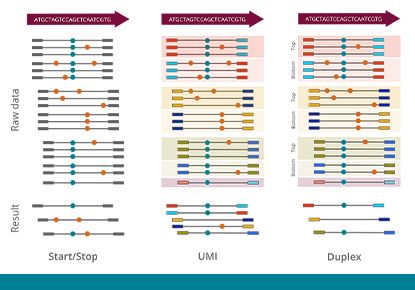
High-sensitivity solutions for liquid biopsy from NGS
by Ben Liesfeld, August 14, 2020
The varvis® software supports various technologies that allow to use NGS for tumor diagnostics or liquid biopsy applications. This enables our users to detect genomic variants at very low-allele frequencies while monitoring a relatively large genomic region.